How to fix Crawling errors in Webmaster tools? | Weboptim
A lot has changed in Webmaster tools in recent years. The Search Statistics and Links to Your Site sections are the two best innovations so far.
Mapping errors section
Webmaster tools can be divided into 2 main parts: website errors and URL errors.
The classification of errors into these two groups is very useful, as there is a distinct difference between errors at the website and subpage level.
- Website-level errors are more serious, as they can ruin the usability of the whole site.
- URL errors are related to a sub-page and are therefore less urgent problems.
The WMT home page gives you a quick overview of our site, with 3 important tools: Crawling Errors, Search Statistics, Site Maps.
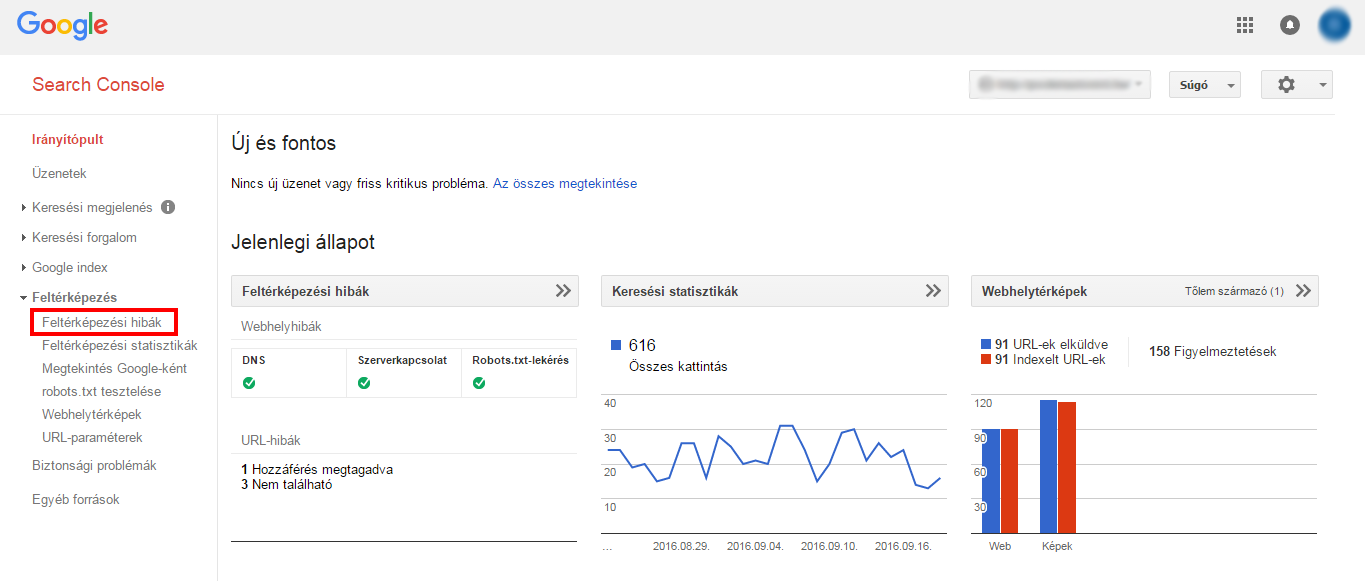
Mapping errors can be easily accessed in the Webmaster Tools interface.
1. Website errors
The Website errors section shows errors for the whole website. These are the highest level errors and should never be ignored. The page shows the data for the last 90 days.
If there has been any activity in the last 90 days, you can see it here:
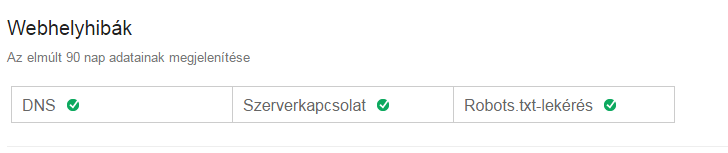
If the site has been error-free in 100% for the last 90 days, then this:

How often do we check these site errors?
Ideally, we should check every day to see if there is a problem. It's a very monotonous job because most days nothing changes, but what if we don't check and miss critical errors?
Check for previous errors at least every 90 days! This section is critical and 100% error-free every day is required.
A, DNA errors
What does it mean?
DNA errors are important. The first and most important errors, because if Googlebot finds a DNS error, it means that Google cannot connect to the domain through the DNS server.
Why is this important?
If a serious DNA problem is detected, action must be taken immediately. DNA is very important as it is the first step to accessing the site. We must take decisive action if we see a DNS error.
How to fix it?
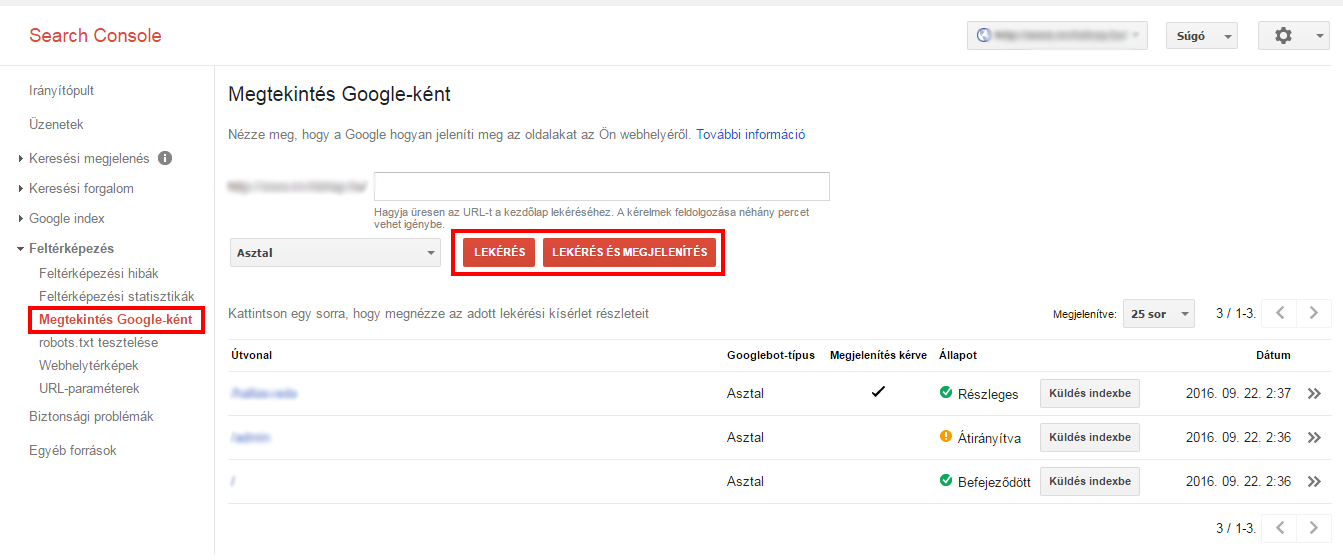
1. First, Google recommends a View as Google tool, where you can see how Googlebot is mapping your site.
2. If you only want to check the DNA status, use the Retrieved from select the option. A Request and Display is a slightly slower process, but it's useful when you want to compare how Google views your page in relation to users.
3. Check your DNS provider. If Google cannot retrieve the page, then further steps are required.
4. Ensure that the server shows error codes 404 and 500. Instead of showing a failed connection, it should show 404 (not found) or 500 (server error).
B, Server errors
What does it mean?
A server error usually means that the server response time is too long and the request has exceeded the allowed time. When Googlebot tries to crawl the page, it will only wait for a certain loading time before it stops. If the load time is too long, it will stop.
Server errors are different from DNS errors. DNS means that Googlebot cannot see the URL due to a DNS problem, while server errors mean that Google can connect to the page but cannot load the page due to a server error.
Server errors can happen when our site gets too many visitors and the server cannot handle the increased traffic.
Why is this important?
Just like DNS errors, server errors are also resolved in a hurry. This is a basic error and has a detrimental effect on the whole website.
How to fix it?
First, make sure that Googlebot can connect to your DNS.
In case the website is running fine and you experience this error, it could mean that there have been server errors in the past. Even if this error has been resolved by now, we need to make changes so that it doesn't happen again.
Google's official guide to resolving server errors:
Use the View as Google tool to see how Googlebot crawls the page. If we query a page and Google displays the main page without any problems, we can assume that Google is able to access the page properly.
Server errors can have several causes/types: timeout, truncated headers, connection recovery, connection denied, connection failed, connection timeout, no response. To fix each error, use the Webmaster Tools Help: https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/35120?hl=en
C, Unsuccessful robots.txt request
An unsuccessful robots.txt request means that Googlebot cannot retrieve the robots.txt file for the website, which is located at the [yourdomain.com]/robots.txt URL.
What does it mean?
One of the most surprising things about the robots.txt file is that you only need it if you want Google not to map certain pages (e.g. admin pages)
Why is this important?
This is a very important question. For smaller, static websites with few changes or new pages, it is not so important. But of course it is worth improving.
But if your site changes content frequently, it's an immediate task to fix the problem. If Googlebot can't download the robots.txt file, it can't crawl the page and so new pages or changes won't be indexed.
How to fix it?
Make sure that the robots.txt file is configured correctly.
Double check which pages you do not want to be crawled.
Triple check the most important line "disallow:/" and ensure that it does not exist unless for some reason you do not want the website to appear in search results.
If the file looks good, but still shows errors, use HTML code checker to see if it returns 200 or 400 HTML codes.
It is better to have no robots.txt file at all than to have one that is not set up properly. If not, Google will crawl as usual. If there is one and it is corrupted, it will stop crawling until the file is fixed.
2. URL errors
URL errors are very different from website errors because they only affect individual pages within a website, not the whole site itself.
Webmaster Tools shows the top URL errors by category - desktop, smartphone. For larger sites this list is probably not enough to identify all errors, but for most sites it can identify all problems.
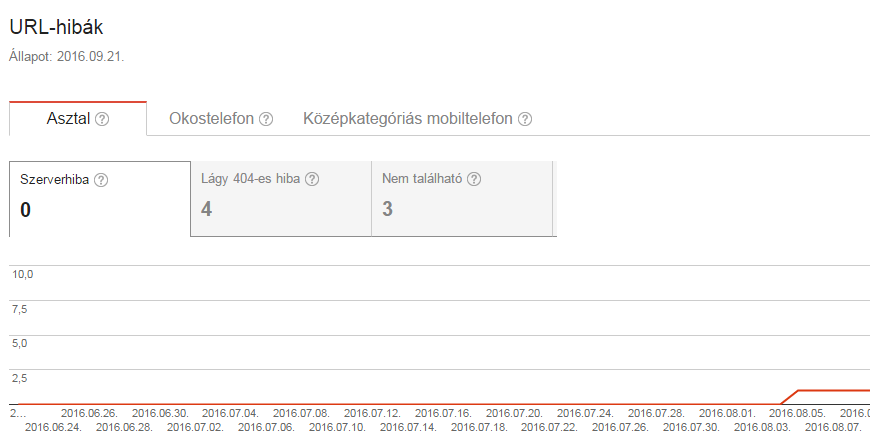
Do we see too many errors? Mark them as corrected!
Many website owners are horrified by the number of URL errors. The most important thing to remember is
- a, Google shows the most important errors only
- b, some of these have already been solved
If you've made some drastic changes to the site to fix errors, or you think a lot of URL errors no longer exist, select Mark as Fixed and check back in a few days.
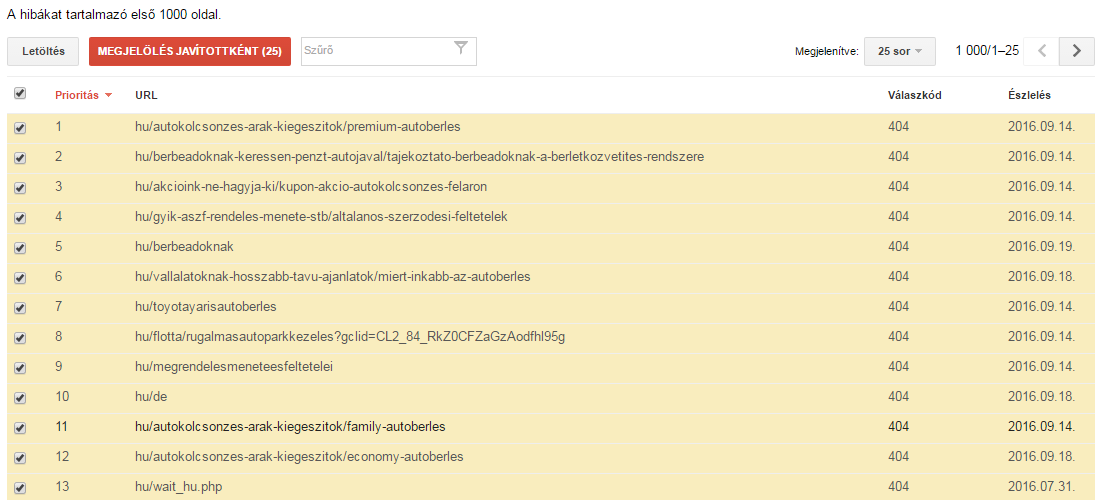
If you do this, the errors will now disappear from the table, and if they have not been corrected, Google will display them again the next time you crawl. If we have indeed fixed the errors, they will not reappear. If the errors still exist, we will know that they are affecting our site.
A, soft 404
A soft 404 error means that the subpage returns 200 (ok) response codes instead of 404 (not found).
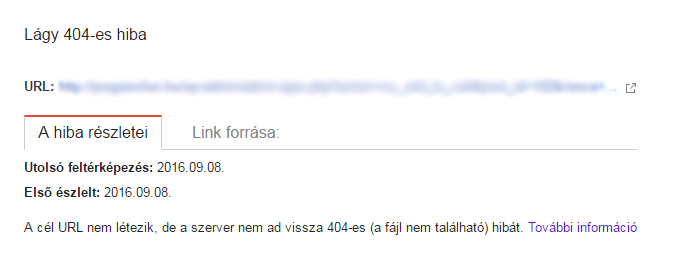
What does it mean?
Just because your 404 page looks like a 404 page doesn't mean it is. The 404 page that a user sees is a piece of content. The visible message lets them know that the page is no longer there. Often, website owners put useful links or funny pictures on the 404 page.
The point of a 404 page is the response you see when crawling. The HTTP response code for the header should be 404 (not found) or 410 (missing).
If the 404 error page is returned and is listed as a soft 404 error, it means that the response code is not 404.
Another situation in which a 404 error may occur is when a 301 redirect points to pages that are not related, such as the main page.
Google's official position:
For a page that does not exist (or is being redirected to the main page), a code other than 404 or 410 HTML can be problematic.
It does give some guidelines, but it is not entirely clear when it is appropriate to redirect the expired page to the main page and when it is not. In practice, if you redirect a lot of pages to the main page, Google may interpret the redirected URLs as soft 404 errors instead of true 301 redirects.
Therefore, if the old page is redirected to a related page instead, it is unlikely to be raised as a soft 404 error.
Why is this important?
If the list of soft 404 errors does not contain critical pages, it is not an immediate task to fix them. If critical pages are listed as soft 404 errors, then quick action is required.
How to fix it?
For sites that are no longer exist:
- Use a 404 or 410 code if the page is no longer there and is not receiving significant traffic or links. Make sure the server response code is 404 or 410, not 200.
- 301 redirects are used to redirect old pages to relevant new pages.
- Do not direct a large number of dead pages to the main page.
For sites that are people living and should not give a 404 soft error:
- Make sure that you have the right amount of content on the page, as too little content can look like a soft 404 error.
- Make sure that the content of the page does not appear to be a 404 page.
The soft 404 is a strange mistake. It can cause a lot of confusion because it is a hybrid of a 404 page and a normal page and therefore cannot always be clearly identified. The key is to make sure that the most important pages are not soft 404 errors.
B, Error 404
A 404 means that Googlebot is trying to crawl a page that does not exist. It also shows a 404 error if another website or subpage links to a page that doesn't exist.
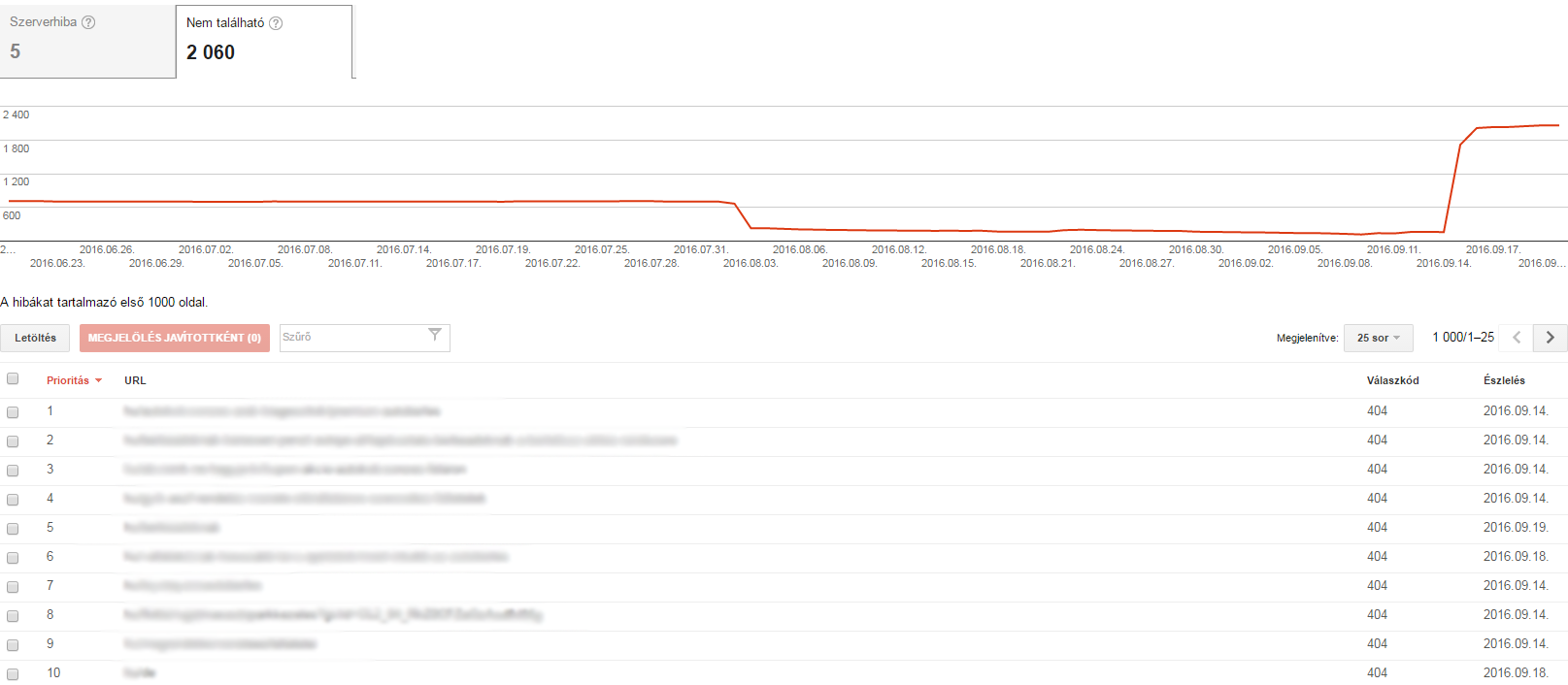
What does it mean?
Google's policy says:
In general, 404 errors have no effect on the Google rankings of a website, so you can ignore them.
This is fine, but if critical pages give 404 errors, we cannot ignore them.
There is a difference between ignoring the problem and staying in the office late into the night to fix it.
A timeless piece of advice:
If you encounter a 404 error, unless the page:
a, many important links from external sources
b, receives a significant amount of traffic
c, has an obvious URL that visitors can easily access,
Let's leave it as 404.
The hardest part of the job is deciding what counts as an important external link and a meaningful amount of traffic for a given URL.
Why is this important?
This is perhaps one of the trickiest and simplest problems that can arise. The huge number of 404 URLs on medium to large sites is enough of a deterrent.
They require an immediate solution when important pages give a 404 error code. As Google has said, if the page has been down for a long time and does not meet the above criteria, then leave it as it is. As painful as it is to see hundreds of errors in Webmaster tools, just ignore them.
How to fix it?
If your important page is showing a 404 error and you don't want to leave it like this, do the following:
- Make sure the page is published and not saved as a draft.
- Make sure that the URL 404 is the correct page and not a variation.
- Check whether the error is visible in the www or no www, http or https version.
- If you don't want to revive the page, but want to redirect it elsewhere, make sure you redirect it to the most relevant page.
In short, if your site is dead, make it alive again. If you don't want to make it alive, 301 it to a good page.
How to stop old 404 pages from appearing in the crawling errors report?
If you no longer need the 404 error page, Google recommends that you ignore it. But to prevent it from reappearing in the Crawling Errors report, there are a few things you can do.
Google shows 404 errors in the first place if there is a link either from within the page or from an external website. In other words, if you type in a URL, it won't show up in the crawl errors unless you get a link from somewhere.
To find out where the bad page is linked from, click on the URL. Then find the link in the source code of the page and fix it.
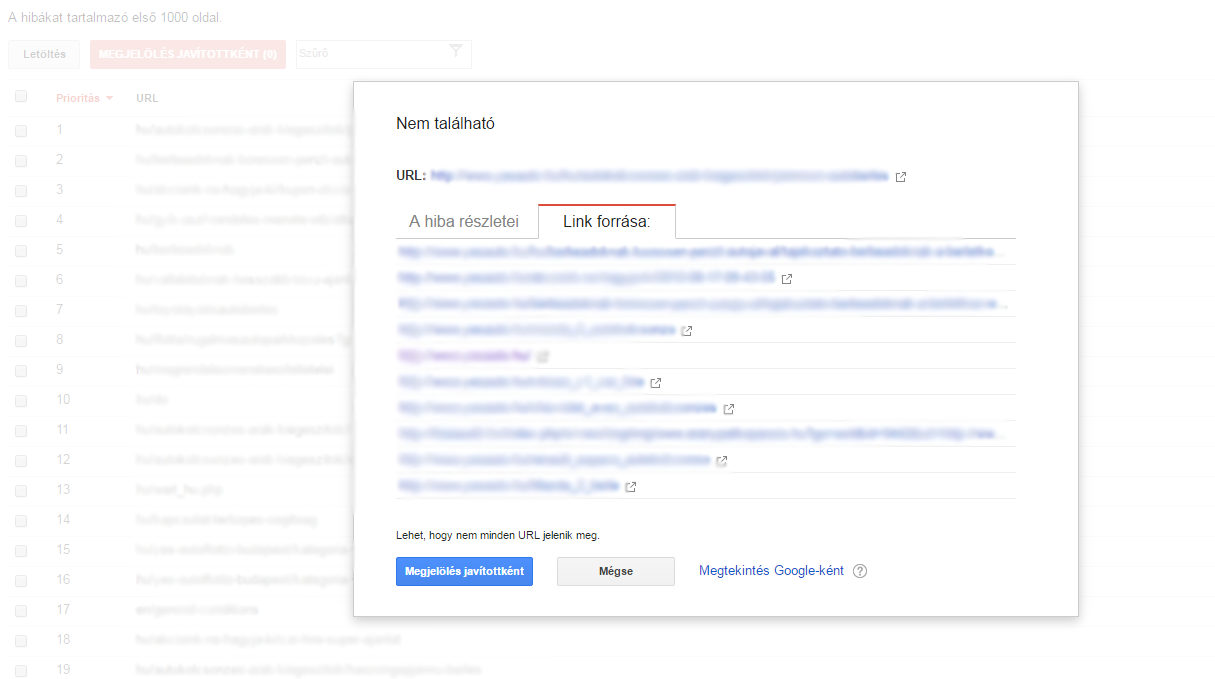
It's tedious work, but if you want to stop the 404 page from appearing in the report, you need to remove the broken link from every page. Even from external websites.
If you receive a link from the old site map, you must remove it from there as well. Do not redirect them to the new sitemap.
C, Access denied
Access denied means that Googlebot cannot crawl the page.
What does it mean?
Denied access errors often block Googlebot in the following:
- We have to ask users to log in to the site to view the URL because Googlebot blocks it.
- The robots.txt file blocks Googlebot, including individual URLs, a folder or even the entire website.
- The hosting provider blocks Googlebot or the server requests proxy-based authentication of users.
Why is this important?
Similar to soft 404 and 404 errors, if it is important for a blocked page to be crawled and indexed, we need to act immediately.
If you do not want the page to be crawled and indexed, you can simply ignore it.
How to fix it?
To fix access denied errors, we need to remove the elements that block Googlebot access:
- Remove the check-in from the pages you want Google to crawl, whether it's an internal page or a pop-up.
- We check robots.txt, we know that the pages that are in it mean that they will be blocked.
- We use the robots.txt checker to see if there are any errors in it and to test specific URLs.
- Use the View as Google tool to find out how your site appears to Google.
While not as common as a 404 error, a denied access error can still damage your site rankings if the wrong pages are blocked.
D, Not followed
What does it mean?
Not to be confused with the "nofollow" link attribute, a not followed error means that Google cannot follow the URL. Most of these errors are caused by Flash, Javascript content or redirects.
Why is this important?
If you encounter a not followed problem with a high priority URL, then yes, it is important.
If the error comes from old URLs that are no longer active, or some of their parameters are not indexed and are just an extra option, then the priority is low - but they should still be analysed.
How to fix it?
Google and other search engines have identified several things that may prevent crawling: JavaScript, Cookies, Unique ID, Frame, DHTML, Flash content
We use the Request and Display tool to see what Google sees. If we, as Google, can't see the page or are missing important content due to one of the above technologies, there's a bug. After all, without visible content and links, the URL cannot be tracked.
If there is a parameter problem, let's check how Google handles our parameters.
The not followed pages are similar to redirects, note the following:
- Check the redirection chains.
- If possible, update the page structure so that all subpages are accessible from a static page.
- The site map should not include the redirected URL, except for the destination URL.
E, Server and DNS errors
Under URL errors, Google lists server and DNS errors once again, just as it does for website errors.
Google's position is that these should be treated in the same way as site-level DNS and server errors.
If you have a separate setting for custom URLs, such as mini-sites, or use a different configuration for certain URLs within your domain, they may appear here.
Summary of mapping errors
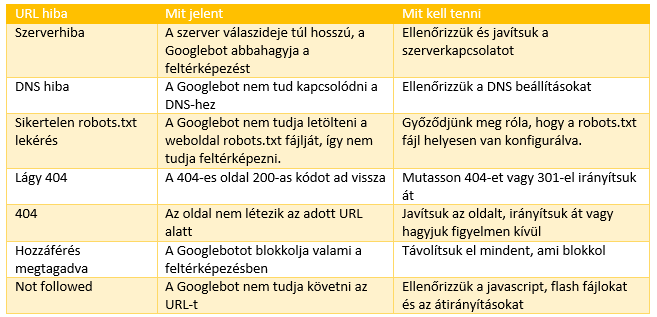
Conclusion
No one wants to go through and fix one by one seemingly insignificant URL errors or, on the contrary, panic when they see thousands of errors in Webmaster tools.
With experience and repetition, we can learn how to react to mistakes: which ones are important and which ones we can safely ignore.
Fixing errors can not only help improve your search rankings, it can also provide a better user experience for visitors and help you achieve your business goals faster.
Source: moz.com