Guide to search engine optimisation for e-commerce websites | Weboptim
There's no question that everyone wants to get ahead of their competitors on Google's results page. But what if you don't know the SEO tricks to get ahead? If we miss out on clicks, we miss out on sales.
Whether you have a new website or an existing site, this guide provides useful tactics for search engine optimisation.
Without a strong SEO strategy, you could lose impressions, clicks and sales.
But how can we improve the rankings of our e-commerce site?
PART 1: RESEARCH
Before we can start any SEO (on-page, off-page) work, we need to do a research or two, keyword and competitor research.
Why?
Research is the most important part of SEO. If you target the wrong keywords, your campaign will bring low quality traffic and few conversions, and no business wants that.
A. Keyword research
There are 3 main areas to focus on in keyword research.
1. Find keywords for your homepage and product pages
When it comes to optimising the most important pages on a website, we need to consider relevance, search volume and ranking difficulty for the keywords.
Choose keywords that:
- that are highly relevant to our brand and products
- that have high exact search volume (locally, not globally) according to Google's Keyword Planner tool
- for which the difficulty level is low
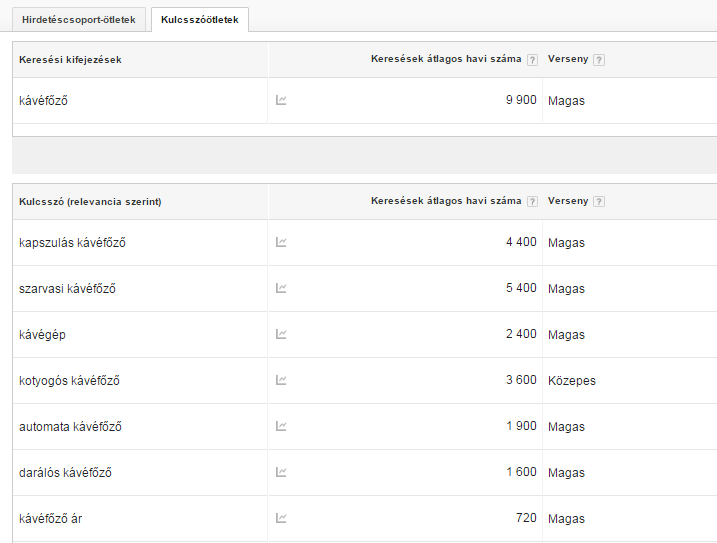
Be careful not to choose words that are too general or too competitive. If the word is too generic, it will have a high bounce rate and a low conversion rate because people will click on the website but not find what they are looking for. Also, if you choose a word that has high competition, it can take a long time to rank well for it (if you can rank well at all).
2. Identify keywords for blog topics
Creating blog content can help improve your website's ranking for additional keywords that don't have space on the main website. Plus long tail keywords can be easily optimised for with a blog.
What are long tail words? They are specific searches that people use to find something. They consist of more than one word.
Look for long tail keywords that have a high search volume and are easy to get ahead of. But! Never clutter the text of your website or blog articles with keywords. When writing a blog, focus on providing good content that people want to read and then want to share with others.
3. Beware of keyword cannibalisation
Keyword cannibalisation is when you try to rank multiple subpages within the same webpage for a given keyword.
So don't write a blog post using keywords that a page on your website is already focusing on. To avoid keyword cannibalisation, list out the subpages of the website on an Excel spreadsheet along with the keywords you want to get ahead of. Sort the keywords, if you are good, no duplication between them.
B. Competitor research
Once you have done the keyword research, you are halfway there. Now it's time for the competitor research.
1. For which keywords are the main competitors ahead?
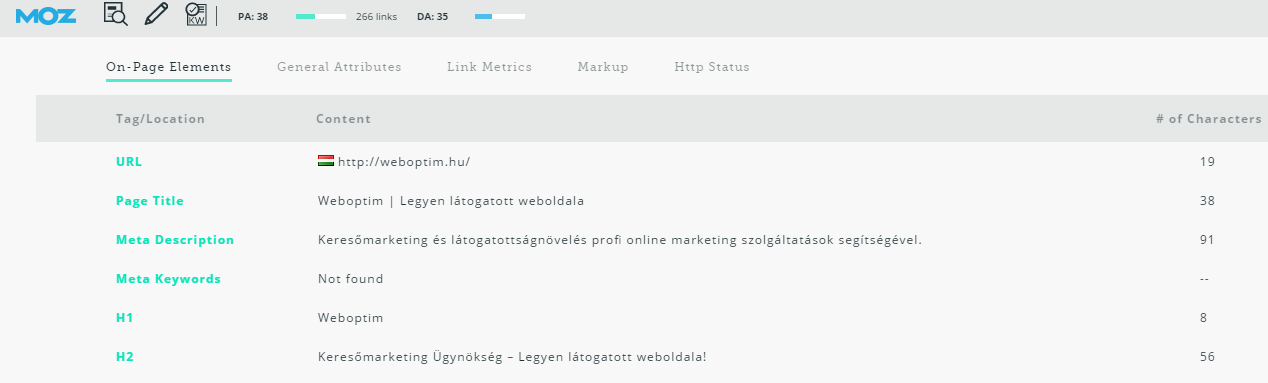
Draw up a list of keywords for which your competitors appear in good positions. We need to see if they have a higher Domain Authority value than us. Does your website have a higher Page Authority value?
If your competitors have a significantly higher DA and PA than you, it might be a good idea to optimize for other keywords, because they can be very difficult to fight. Try to win more simply if you can!
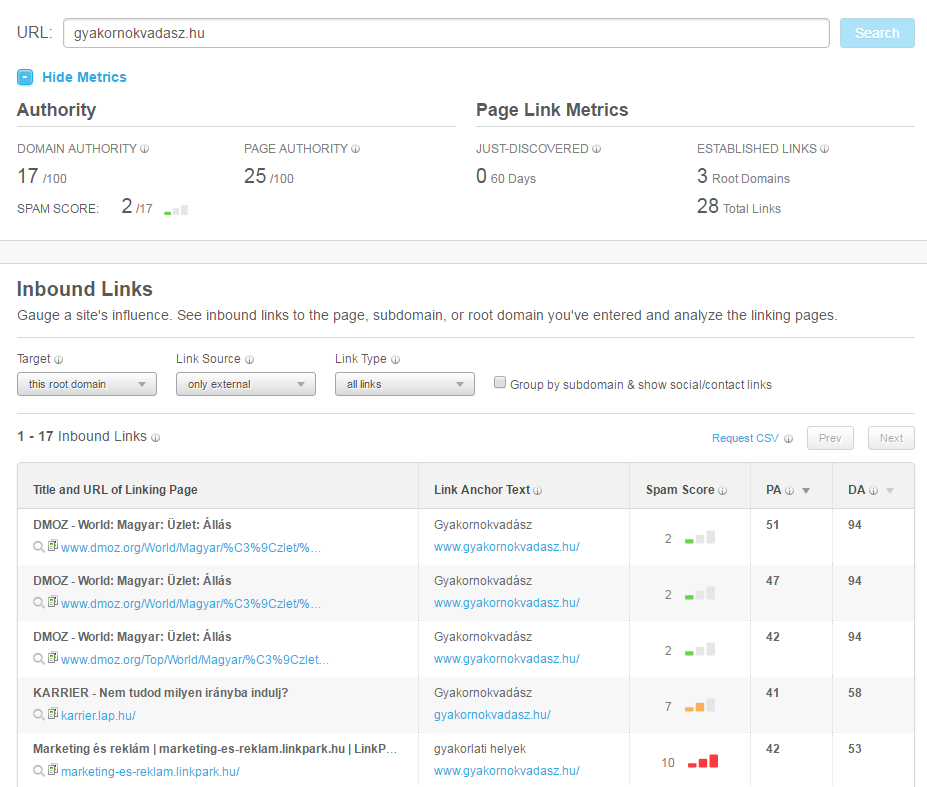
2. Where do they get their links from?
It is important to collect the places from which competitors receive inbound links. We should try to get links from these sites ourselves, e.g. visit the blogger, create our own company page, etc..
Before doing this, delete websites with a low DA value from the list. Links from such sites can have a bad effect on our Google rankings, because Google might think that if bad sites link to us because we are a bad site.
3. What does the structure of your website look like?
Let's look at the structure of competing websites. How does their navigation look? How deep do their links point? When considering the structure of e-commerce sites, we should pay particular attention to the following:
- popular products in a given category
- related products
- best rated products
- last viewed products
Once we know how big companies organise their websites, we can decide to follow the same path or we can choose a completely different path. But just because the big competitors have deep internal navigation, we don't have to copy them.
PART 2: IDENTIFYING PROBLEMS
Once we've done the keyword and competitor research, it's time to start looking at the problems with our website. Here are some things to focus on:
A. Quickly find website errors
Common but quickly correctable errors include:
- redirect 404 pages to the appropriate current content
- change 302 redirections to 301
- update duplicate pages, meta title and meta description data
B. Determine the speed of the website
Visitors will not wait for a slow website to load. Customers will return to Google's results page and look for a faster website, probably a competitor.
Research shows that 40% of people will quit if a web page takes more than 3 seconds to load. Don't lose customers because the site is slow!
If your site loads in more than 3 seconds, improve the speed by using a different CMS system, more server space or reducing the size of images and files.
PART 3: ON-PAGE OPTIMISATION
While we know that off-page optimisation (link building) is important, on-page optimisation is just as important. It includes all the elements within a website that can help improve rankings.
For on-page optimisation, focus on the following 8 things:
- keyword optimization
- site structure
- internal links
- usability
- mobile version
- customer feedback
- rich snippet
- social media integration
A. Keyword optimisation
To optimise keywords, we need to ensure that the keyword is present in strategic places, including:
- page title
- Headlines
- subtitles
- Paragraphs
- product description
- picture names
- pictures alt text
- meta title and description
- URL
When creating a URL, make sure it is user-friendly. This means it should contain real words (keywords) and not numbers or characters.
Also, remember that the meta title and description should not be gibberish or full of keywords. They should be treated as an advertisement, which can lead to higher click-through rates and better Google rankings.
B. Site structure
When building a website from scratch or redesigning a website, the use of an information structure is mandatory. A good structure can have a significant impact on website usability, rankings and conversions.
Focus on creating a simple website structure, which means that it should be possible to get from the main page to the product pages with just a few clicks. In this way, link strength is shifted from the home page to the product pages through internal links.
Then, take the keywords, pair the words and subpages together in a way that serves visitors and search engines, showing a logical path from the main page to the product pages.
C. Internal links
Internal linking is when you link from one sub-page of a website to another. Internal links can be assigned their own link text, which can also help improve rankings for keyword links.
Internal linking should be done "sparingly". If all pages are loaded with internal links, Google will perceive them as suspicious. Google is smart, its algorithm will spot such actions immediately. Place internal links where they look relevant and natural.
Do not use the same link text for many internal links (Google looks for variation in link text for both external and internal links).
D. Usability
Usability is super important for SEO and keeps users happy. If your e-commerce website is usable, users will visit it, and that's the goal.
A good user experience means that the website is simple, easy to use and useful. It also means that users will spend more time on the site.
E. Mobile version
Many people not only browse the web, but also shop via a mobile device, which means it's important to have a mobile-friendly version of your website.
In the past, many companies questioned creating a mobile version because it could cause duplication problems, leading to SEO issues and affecting Google search rankings.
However, with the advent of responsive web design, we can now create a website that works well on all devices (laptop, mobile tablet) without having to create multiple sites. This is good news for e-commerce websites.
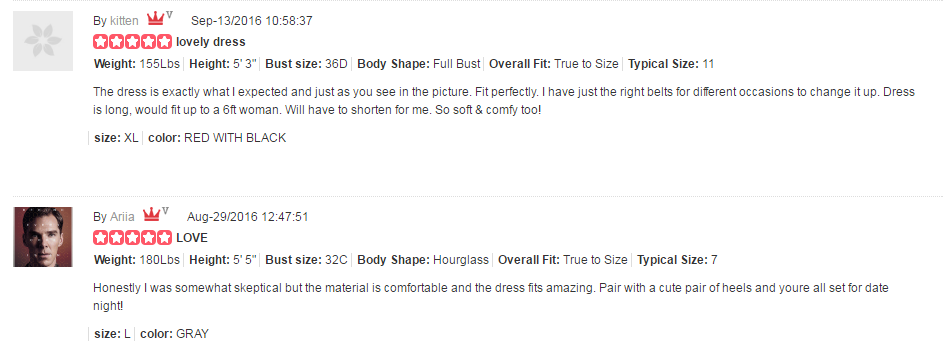
F. Customer feedback
Of course, customer feedback is very important for e-commerce sites, as it can increase the conversion rate.
In addition to increasing conversions, reviews also have a positive impact on SEO because more reviews = more content and more frequent reviews = fresh content that Google likes. 🙂
To collect reviews, we can use a plugin or send out an email a few days after the purchase asking customers if they need any help and if not, we ask them to write a review.
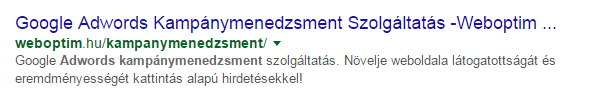
G. Rich snippet
Snippets are the few lines of information (title, URL, description) that appear for each web page in Google searches. In some cases, depending on the search term, this may of course be supplemented with additional information, e.g.
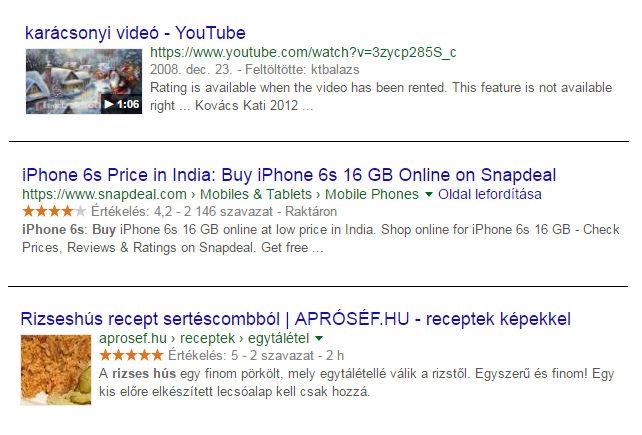
These are called rich snippets and have a big impact on the ranking of a website. There are different types of snippets for authors, company information, events, people, products, recipes, videos, etc..
Rich snippets are actually HTML codes that tell search engines what users need to know about a website without clicking on it.
When people see images in Google results, they are more likely to click and buy.
H. Social media integration
An e-commerce site cannot be complete without social media integration. Social media signals (shares, likes, engagement) have an impact on SEO.
If we have a lot of social signals, it tells Google that people find our website and brand valuable. We can easily increase the number of social signals by adding social buttons to product pages, blog articles, main page.
PART 4: ADDITIONAL TESTS
Once the on-page optimisation has been done, the following should be done:
- use analytics to know which keywords convert best
- use PPC campaigns to find the best converting words for your SEO strategy
- test meta titles and descriptions to increase click-through rates
- perform A/B testing on pages to increase conversions
A strong testing strategy can help to further improve results. Without constant, ongoing monitoring, placements may fall and sales may decline or sales may show poor conversion rates.
PART 5: ADDING BLOG CONTENT
Since each page of the website should be optimised for only one keyword, there will be a lot of keywords that are not listed anywhere on the page. To get ahead of these keywords, a good solution is a blog. Just like a website, blog posts should be high quality and reader-friendly.
If your post is full of keywords or low quality, visitors will not read it, they will not share it. And Google can even penalize us for keyword stuffing.
PART 6: LINK BUILDING
Similar to content, we need to focus on getting quality inbound links.
Not only will Google penalize you if you have a lot of low quality pages linking to you, but the referring traffic will not add anything positive to your business.
A poor quality link may come from a site with poor authority. We can often tell at a glance whether a page is low quality: such pages are full of ads, short content, keyword stuffing.
Link farms often provide low quality links, so beware of them.
Instead, focus on getting links from good, high authority sites by offering them something valuable in return for a link. We can offer high quality guest posts, stories, help with a research project, shared infographics, and so on.
Some types that are suitable for e-commerce websites:
- product reviews
- mentions
- excellent content
- broken link building
What not to do:
- use the same link text all the time - aim for variety
- link to the same subpage - link to the most relevant subpage
- link acquisition from low authority sites
Of course, we don't always have control over the link text or which subpages are the best, but that's okay.
PART 7: LOCAL BUSINESS TIPS
Are we a local business? Let's make sure that the triad of name, address, phone number (NAP) appears in every place on our website where it can. This information can be submitted to local strong aggregator sites as well as industry specific link aggregators if relevant.
Location-based keywords can also be used in meta descriptions.
This is important because Google combines local and organic search rankings.
Summary
There are many reasons to optimise your website, but the main goal is to increase sales.
If you do SEO right, you can experience increased, quality traffic, which can lead to more conversions and return visitors.
Before we get started, let's understand one thing: SEO work is not a one-off, casual thing. Google and other search engines are constantly updating their algorithms in order to provide search users with the best results. For this reason, we need to stay up to date on updates and develop our strategy accordingly.
There is no doubt that SEO work takes a lot of time and energy, but the benefits make it worth it.
Source: blog.kissmetrics.com